What is the Pythagorean Theorem?
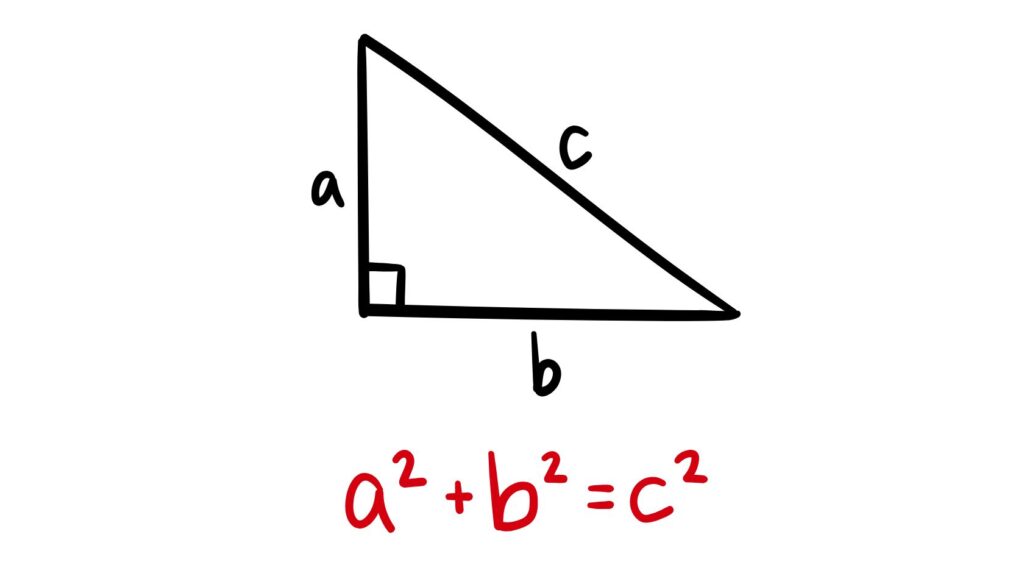
The Pythagorean theorem is a popular geometric theorem that shows that if you have a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side (the longest side of a right-angled triangle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
The Pythagorean theorem can be credited to the Greek Mathematician Pythagoras of Samos. He was an ancient Greek philosopher who established a community of mathematicians who lived like monks and worked fervently with numbers. While experts believe that Pythagoras introduced the theorem, the theorem was actually already in use a millennium before Pythagoras was born.
Using the Pythagorean Theorem
To better understand, let’s address this theorem and what it is for? This geometric theorem is used to find the length of a right triangle’s unknown side. People can see the formula for the base, perpendicular, and hypotenuse using this theorem.
So, the formula is shown as a² + b² = c². In this formula, “a” represents one leg of the right triangle (often called the base), “b” represents the other leg (often called the perpendicular or height), “c” represents the hypotenuse, which is the longest side of the triangle and always opposite the right angle.
Summary
- The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
- This theorem is used to find the unknown side of a right triangle through the formula: a² + b² = c²
—–
So, the next time someone asks you, “What is the Pythagorean Theorem?” you know the answer. Keep it up, young genius!
Need more help in Math? Got assignments to finish? Let us help you excel in school. Ask your questions here, and our team will try to answer them and share more information with you.